Carrom-playing Robot Arm
Construction and programming of 5-DOF robot arm to play Carrom, a game similar to 8-ball, ME/EE/CS 134: Advanced Robotics: Planning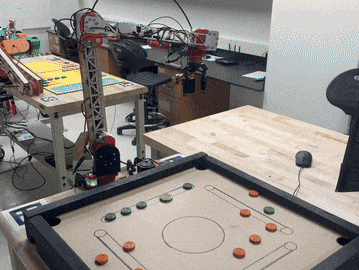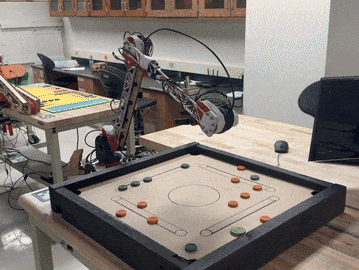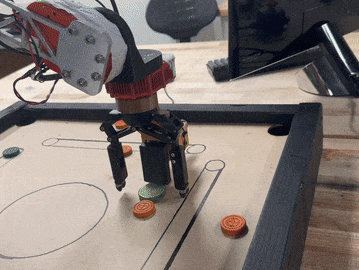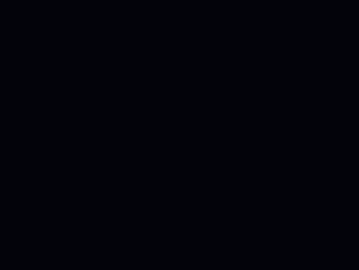
Construction and programming of 5-DOF robot arm to play Carrom, a game similar to 8-ball, ME/EE/CS 134: Advanced Robotics: Planning
Occurpancy grid-based exploration algorithm via optimizing for information gain and cost-to-go for ME/CDS 234b Advanced Robotics: Planning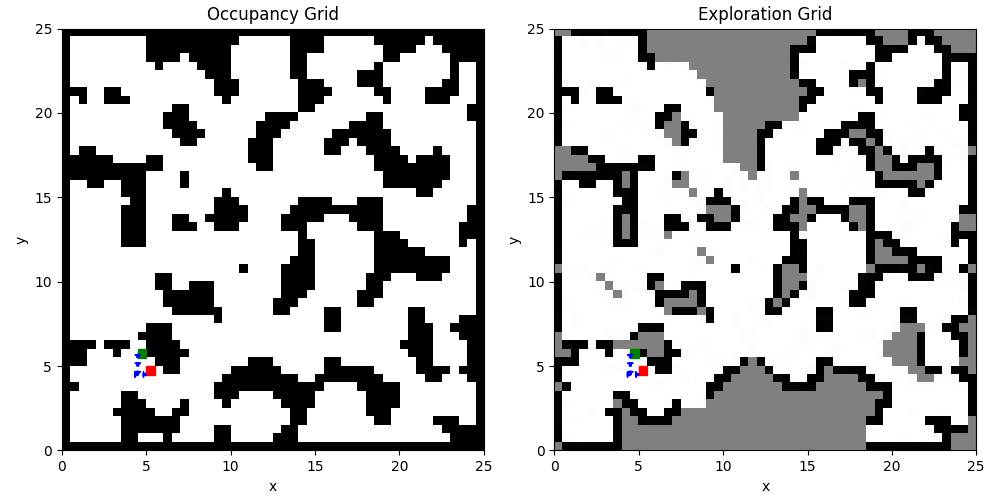
Compared D* with other graph search algorithms on large graphs to determine computation speed-up for ME/CDS 234a Advanced Robotics: Planning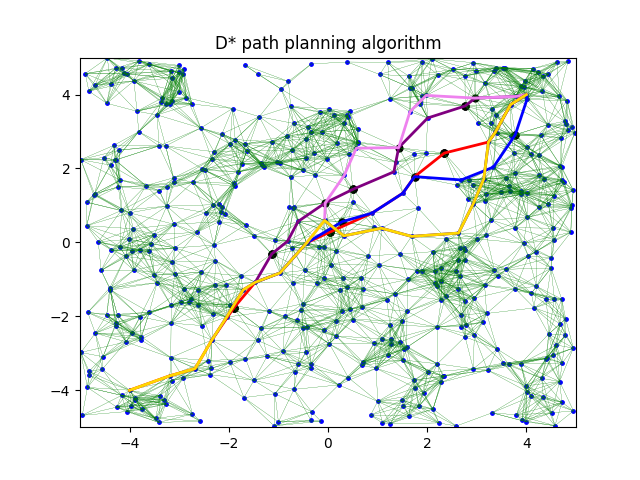
Hardware implmentation of localization, mapping, and path planning algorithms for ME/EE/CS 169: Mobile Robotics
Hierarchical PRM-based planner for quadruped walking on various environments, ME/EE/CS 133b: Robotics: Planning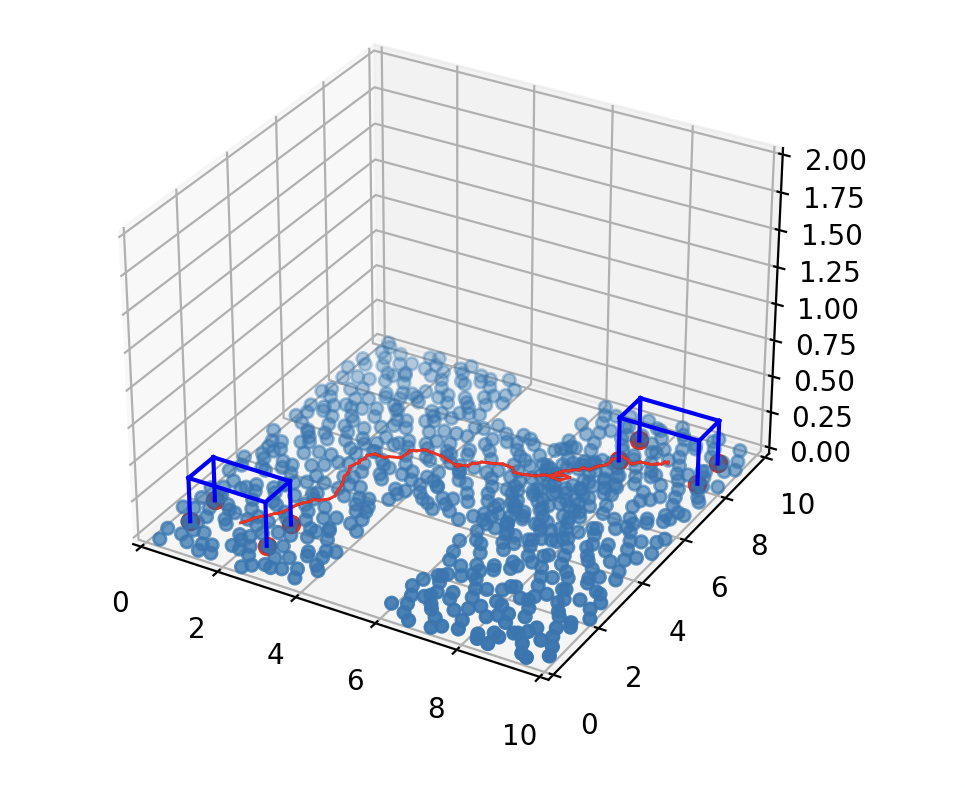
ROS kinematic demonstration of 30-DOF quadruped, designed in Solidworks, ME/EE/CS 133a: Robotics: Kinematics 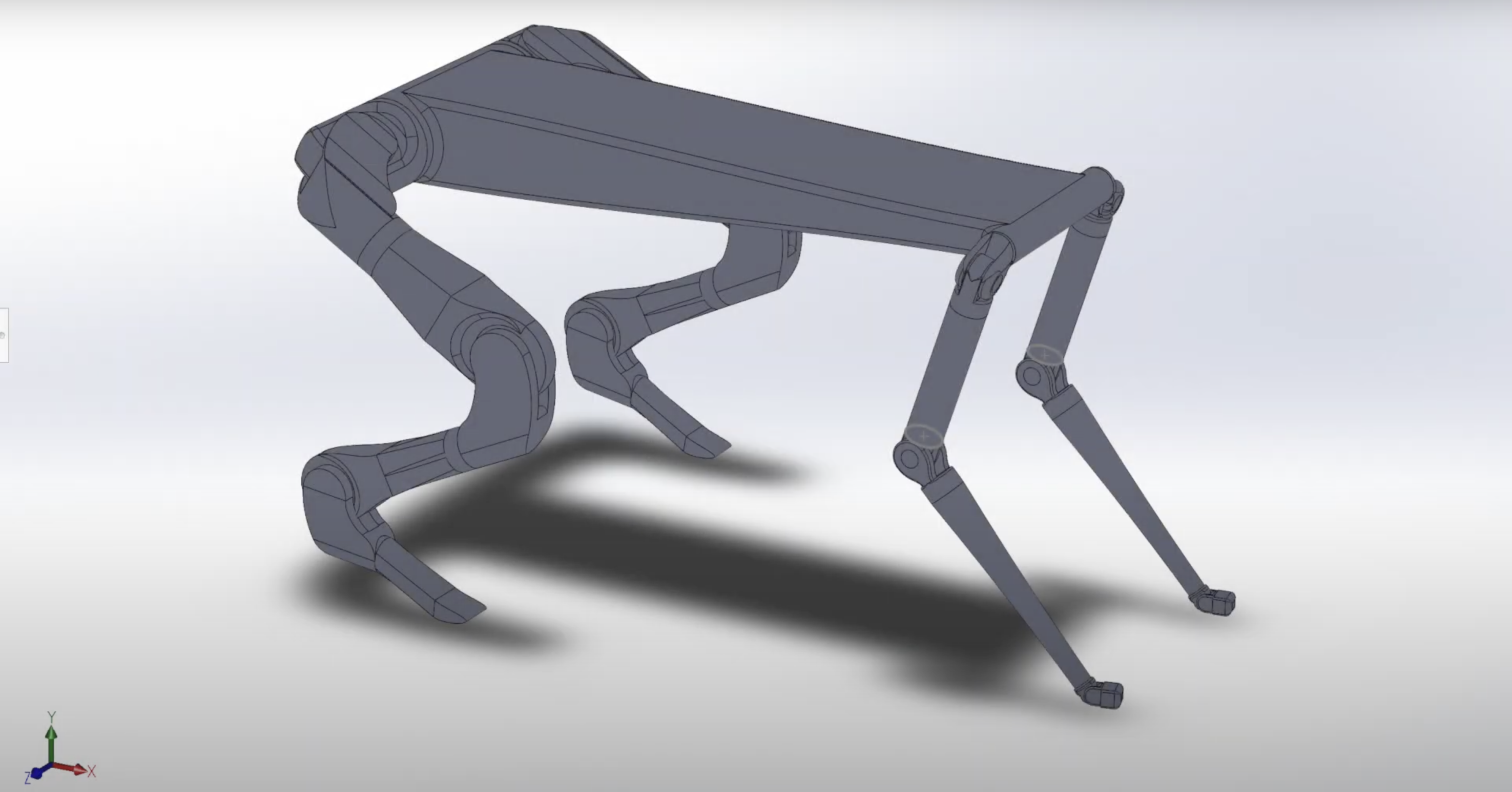
currently in progress, 2023
Recent advancements in flexible materials provide potential mechanisms towards transforming powered ankle exoskeletons from being heavy and rigid towards being lightweight and flexible. Specifically, this work presents a novel ankle exoskeleton that utilizes a pair of handed shearing auxetics coupled with compression springs. This flexible mechanism converts rotation into a linear displacement, effectively changing the stiffness of the spring during the walking gait. By controlling this stiffness properly, the ankle exoskeleton achieves lower muscle activity during toe push-off.
Accepted to ICRA, 2024
Ensuring robot safety in complex environments is a difficult task due to actuation limits, such as torque bounds. This paper presents a safety-critical control framework that leverages learning-based switching between multiple backup controllers to formally guarantee safety under bounded control inputs while satisfying driver intention. By leveraging backup controllers designed to uphold safety and input constraints, backup control barrier functions (BCBFs) construct implicitly defined control invariance sets via a feasible quadratic program (QP). However, BCBF performance largely depends on the design and conservativeness of the chosen backup controller, especially in our setting of human-driven vehicles in complex, e.g, off-road, conditions. While conservativeness can be reduced by using multiple backup controllers, determining when to switch is an open problem. Consequently, we develop a broadcast scheme that estimates driver intention and integrates BCBFs with multiple backup strategies for human-robot interaction. An LSTM classifier uses data inputs from the robot, human, and safety algorithms to continually choose a backup controller in real-time. We demonstrate our method’s efficacy on a dual-track robot in obstacle avoidance scenarios. Our framework guarantees robot safety while adhering to driver intention.
Download here
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
CS 12 Section 9, California Institute of Technology, Computing and Mathematical Science Department, 1900
CS 12: Section 9, Introduction to Prototyping is a 3-unit, pass/fail course I designed taught in Winter term that provides a low-stakes, novel opportunity to learn about prototyping. The course's objectives are twofold; (i) to provide a stepping stone to more advanced robotics, mechanics, and computer science courses for students of any major, and (ii) to provide real, applicable experience in prototyping and design.
Introduction to Prototyping will provide a low-stakes, multidisciplinary experience in robotics that students may use to guage their interest in robotics. This 3-unit pass/fail course will enable students to prepare for SURFs and internships during the school year without disrupting their regular academic schedule. This is especially important for Caltech undergraduates, who are often the most common applicants for SURFs, as it enables them to gain practical prototyping experience while satisfying their important major requirements. Introduction to Prototyping will also provide a stepping stone to more advanced clubs, research and classes on campus.